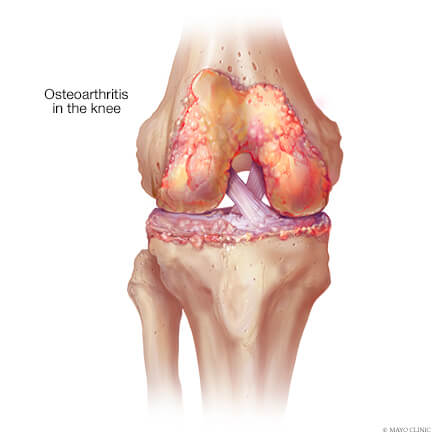
Knee osteoarthritis is a common condition that occurs when the protective cartilage in the knee wears down, while bone around the joint grows or loses its normal smooth contours. Knee osteoarthritis symptoms may develop slowly or come on relatively quickly. Common symptoms include:
- Pain, Your knee may hurt during or after movement
- Tenderness. Your knee may feel tender to touch
- Stiffness. Knee stiffness may be most noticeable when you wake up in the morning or after a period of inactivity
- Loss of flexibility. You may not be able to move your knee through its full range of motion
- Grating sensation. You may hear or feel a grating sensation when you stand up, walk, or climb stairs
- Bone spurs – extra bone growth around the knee may feel like hard lumps
The cause of knee osteoarthritis is not well understood, but risk factors include:
- Older age
- Female gender
- Obesity
- Prior knee injury (e.g., ACL or meniscus injury)
- Certain occupations or sports that place high stress on the knees
- Genetics
- Abnormal joint alignment
The diagnosis of knee osteoarthritis starts with a careful history and physical examination. Imaging is often recommended, starting with plain radiographs (X-rays). Sometimes your provider will recommend more advanced imaging, such as MRI. Occasionally blood tests or joint fluid analysis are used to rule out other types of arthritis related to inflammatory or infectious conditions.


